Class 12, Chemistry, Practical
Preparation of Double Salt
* Mohrs Salt, * Potash Alum
What is an inorganic compound?
Inorganic compounds are substances that do not come from living things. They are formed by non-living natural processes or by laboratory preparation methods. The branch of chemistry that deals with the behaviour and properties of inorganic compounds is called Inorganic Chemistry. Inorganic compounds are found in nature in the form of minerals.
What are the different types of inorganic compounds?
The two important classes of inorganic compounds are Coordination Compounds and Double Salts.
Coordination compounds (complex compounds)
Complex compounds are formed by a large number of transition metals in which the metal atom is bound to neutral molecules or to negatively charged species called ligands. The elements of group 3-12 are called transition metals.
These compounds are also called coordination compounds. The ligands donate electrons to the metal atoms and the metal atoms accept these electrons to form a ligand-metal coordinate bond. The number of ligands directly bonded to the central metal atom is called the coordination number of a complex. The structure of coordination compounds was first proposed by Alfred Werner. He proposed the concept of a primary valence and secondary valence for a metal ion. Primary valences are satisfied by the central ions and secondary valences are satisfied by the ligands. Secondary valence is equal to the coordination number.
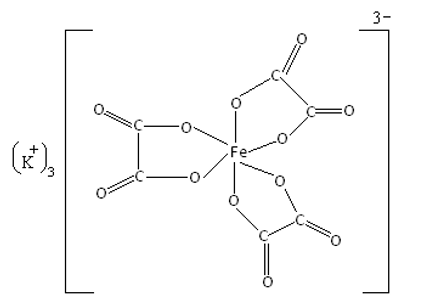
On example is Potassium trioxalatoferrate (III) { K3[Fe(C2O4)3].3H2O}
Potassium trioxalatoferrate (III) is a coordination compound. In this complex, iron is the central metal ion and oxalate [(C2O4)2-] is the ligand. Oxalate is a bidentate ligand in which two oxygen atoms donate electrons to the central iron atom. It is an octahedral transition metal complex in which iron is in the +3 oxidation state. So we can say that in complex potassium trioxalatoferrate (III), the central Fe3+ ion is octahedrally surrounded by bidentate oxalate ligands. Potassium acts as the counter ion, and the Fe3+ ion, along with the ligand, constitute the coordination sphere. The structure is shown below.